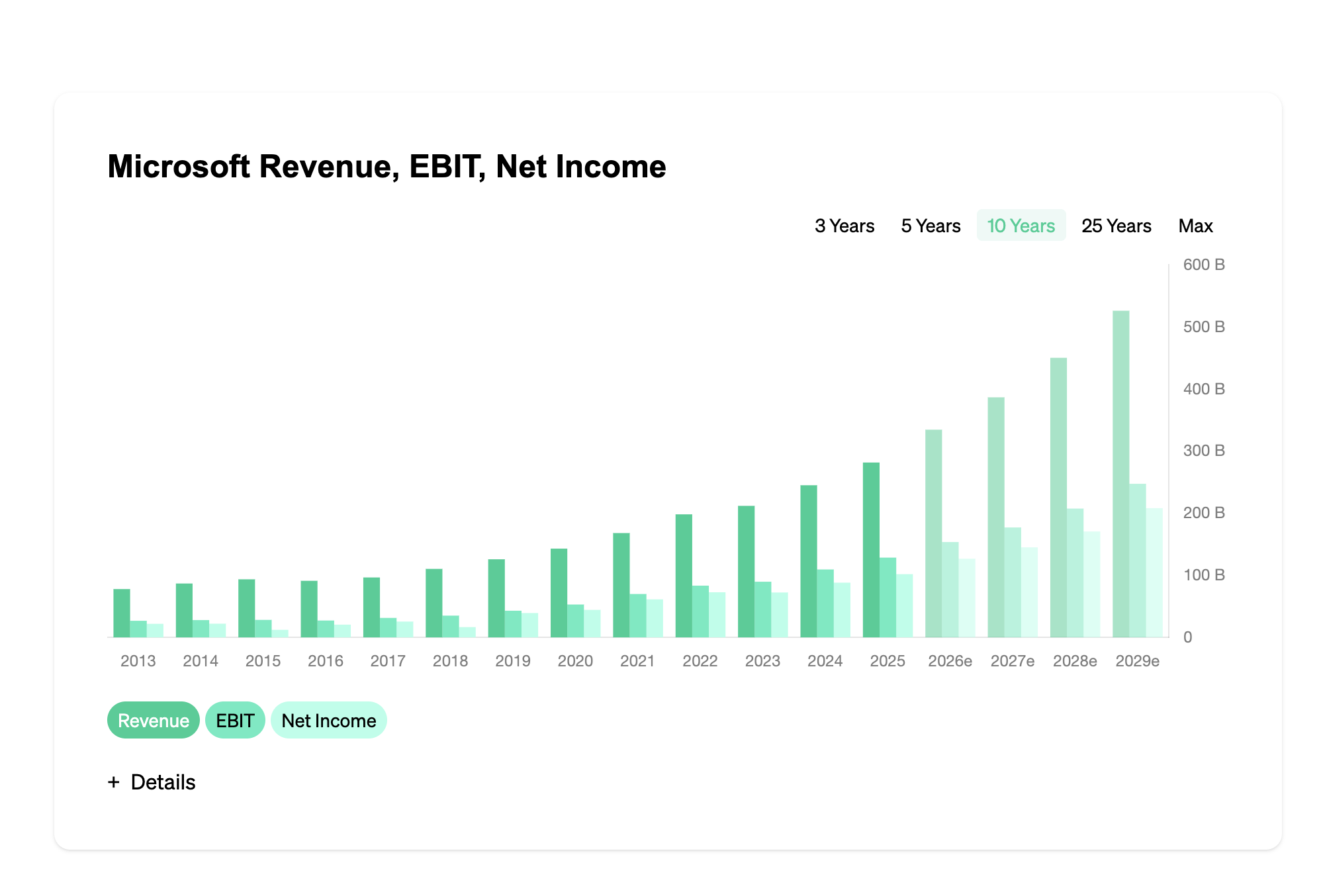
NIC
Definition und Erklärung
TL;DR – Kurzdefinition
Zu den FAQs →NIC: NIC is the acronym for Net Interest Cost, also known as Nettokostensatz in German. It is a significant measure utilized in capital markets, particularly within the realm of fixed-income securities. NIC represents the total borrowing cost to an issuer of a bond or loan after adjusting for the present value of all cash flows associated with the transaction, including any discounts or premiums. The calculation of NIC involves several key components. First, it takes into account the stated interest rate at which the bond or loan is issued. This rate is typically expressed as a percentage of the face value and determines the periodic interest payments made by the issuer. Secondly, NIC considers the time value of money by discounting those interest payments to their present value. This is accomplished by applying an appropriate discount rate, typically based on market interest rates or the specific credit risk of the issuer. Moreover, NIC incorporates any additional costs or rebates associated with the issuance of the bond or loan. Such costs may include underwriting fees, commissions, legal expenses, or other administrative charges. The inclusion of these expenses ensures the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the overall borrowing cost estimation. Investors heavily rely on NIC to gauge the true expense associated with fixed-income investments. By considering all relevant costs and present valuing future cash flows, NIC provides a reliable benchmark to compare different investment opportunities within the capital markets. This allows investors to make informed decisions based on the net cost to the issuer and the potential yield or return they can expect from the investment. In summary, Net Interest Cost (NIC) measures the total borrowing cost for an issuer of a bond or loan, accounting for the present value of all cash flows, adjustments, and additional costs incurred during the transaction. By evaluating the NIC, investors gain valuable insight into the actual expenses associated with fixed-income investments, aiding them in making informed investment decisions. At Eulerpool.com, a premier destination for equity research and finance news, we strive to provide the most comprehensive and accurate glossary/lexicon for investors in capital markets. Be sure to explore our website for further information and an extensive range of resources tailored to your investment needs.
Ausführliche Definition
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu NIC
Was bedeutet NIC?
NIC is the acronym for Net Interest Cost, also known as Nettokostensatz in German. It is a significant measure utilized in capital markets, particularly within the realm of fixed-income securities.
Wie wird NIC beim Investieren verwendet?
„NIC“ hilft dabei, Informationen einzuordnen und Entscheidungen an der Börse besser zu verstehen. Wichtig ist immer der Kontext (Branche, Marktphase, Vergleichswerte).
Woran erkenne ich NIC in der Praxis?
Achte darauf, wo der Begriff in Unternehmensberichten, Kennzahlen oder Nachrichten auftaucht. In der Regel wird „NIC“ genutzt, um Entwicklungen zu beschreiben oder Größen vergleichbar zu machen.
Welche typischen Fehler gibt es bei NIC?
Häufige Fehler sind: falscher Vergleich (Äpfel mit Birnen), isolierte Betrachtung ohne Kontext und das Überinterpretieren einzelner Werte. Nutze „NIC“ zusammen mit weiteren Kennzahlen/Infos.
Welche Begriffe sind eng verwandt mit NIC?
Ähnliche Begriffe findest du weiter unten unter „Leserfavoriten“ bzw. verwandten Einträgen. Diese helfen, „NIC“ besser abzugrenzen und im Gesamtbild zu verstehen.
Preferințele cititorilor în dicționarul bursier Eulerpool
Günstigerprüfung
Günstigerprüfung ist ein Begriff, der in der deutschen Steuerwelt verwendet wird, insbesondere im Zusammenhang mit Investoren in Kapitalmärkten. Diese Prüfung bezieht sich auf die Überprüfung von Kapitalerträgen, um festzustellen, ob...
Lagemaß
Lagemaß bezeichnet ein weit verbreitetes statistisches Maß, das in der Kapitalmarktforschung Verwendung findet. Es dient dazu, die systematischen Abweichungen eines Finanzinstruments von einem bestimmten Vergleichsmaßstab zu quantifizieren. Im Allgemeinen ermöglicht...
Verkehrs-Rechtsschutzversicherung
Die Verkehrs-Rechtsschutzversicherung ist eine Versicherungspolice, die finanziellen Schutz bietet, wenn rechtliche Streitigkeiten im Zusammenhang mit dem Straßenverkehr auftreten. Sie deckt eine breite Palette von Rechtsangelegenheiten ab, die im Zusammenhang mit...
Lean Marketing
Lean Marketing (Schlankes Marketing) ist eine effiziente und kostenbewusste Marketingstrategie, die darauf abzielt, die Ressourcen eines Unternehmens optimal zu nutzen, um seine Marktpräsenz zu maximieren. Diese Methode wurde ursprünglich im...
Kreditrevision
Kreditrevision ist ein wesentlicher Bestandteil des Risikomanagements im Finanzsektor. Es handelt sich um einen Prozess, der von Finanzinstituten durchgeführt wird, um die Kreditqualität und -portfolios zu überprüfen und mögliche Risiken...
Preisnehmer
Preisnehmer ist ein Begriff, der in der Finanzwelt häufig verwendet wird, um eine Person oder eine Einheit zu beschreiben, die auf dem Markt nachfragt und daher die Preise für bestimmte...
Brutto-Grundfläche
Brutto-Grundfläche ist ein wichtiges Konzept, das in der Immobilienwirtschaft verwendet wird, um die Gesamtfläche eines Gebäudes oder einer Immobilie zu beschreiben. Es handelt sich um die summierte Fläche aller Geschosse...
Sozialbilanz
Sozialbilanz: Definition, Bedeutung und Anwendung in den Kapitalmärkten Die Sozialbilanz ist ein konzeptionelles Instrument zur Messung und Bewertung der sozialen Auswirkungen einer Organisation oder eines Unternehmens auf die Gesellschaft und ihre...
Alternativverhalten, rechtmäßiges
Das "Alternativverhalten, rechtmäßiges" bezieht sich auf eine rechtliche Handlung oder Entscheidung, die von einer Person oder einem Unternehmen getroffen wird, um auf eine bestimmte Situation oder ein spezifisches Problem zu...
Depotaktien
Depotaktien, auch als Inhaberaktien bezeichnet, sind eine Form von Aktien, bei denen kein Eintrag im Aktienbuch des Unternehmens vorgenommen wird. Stattdessen werden sie direkt im Depot des Aktionärs verwahrt. Dies...