Validity
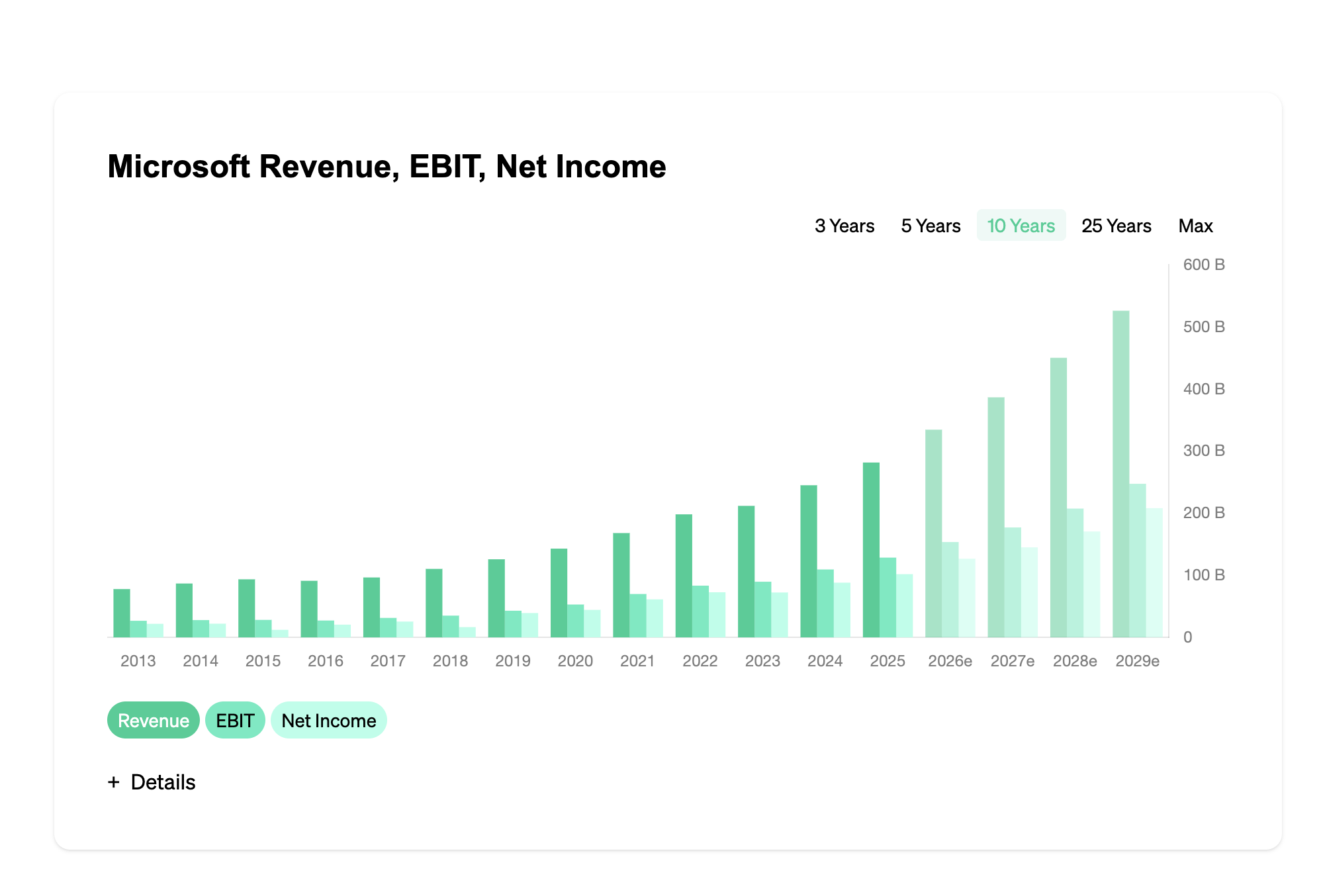
DeFi Analytics
| Exchange | Market Pair | Price | +2% Depth | -2% Depth | Volume (24H) | Volume % | Type | Liquidity Rating | Last Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dex-Trade | VAL/USDT | 0.61 | 324.8 | 913.42 | 10,552.96 | 0.01 | cex | 124 | 7/9/2025, 4:21 AM |
| P2B | VAL/USDT | 0.61 | 0 | 0 | 5,426.58 | 0 | cex | 1 | 7/8/2025, 1:00 PM |
| Upbit | VAL/BTC | 0.6 | 2,110.86 | 2,595.81 | 2,014.15 | 0 | cex | 94 | 7/9/2025, 4:23 AM |
| LATOKEN | VAL/USDT | 0.61 | 790.32 | 700.68 | 1,710.09 | 0 | cex | 21 | 7/9/2025, 4:18 AM |
| Finexbox | VAL/USDT | 0.62 | 0 | 0 | 392.37 | 0.01 | cex | 1 | 7/8/2025, 11:42 AM |
| Finexbox | VAL/BTC | 0.76 | 0 | 0 | 285.32 | 0 | cex | 1 | 5/28/2025, 9:24 AM |
| Nonkyc.io Exchange | VAL/BTC | 0.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | cex | 1 | 4/8/2025, 4:35 AM |
| Dex-Trade | VAL/BTC | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | cex | 1 | 6/2/2025, 1:54 PM |
| Nonkyc.io Exchange | VAL/USDT | 0.66 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | cex | 1 | 4/8/2025, 4:35 AM |
| FreiExchange | VAL/BTC | 0.67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | cex | 1 | 7/9/2025, 4:21 AM |
Validity FAQ
Validity (VAL) distinguishes itself in the cryptocurrency arena with its two-tiered architecture, integrating the Validity blockchain and the Validity Smartchain. The Validity blockchain utilizes a proof of stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, enabling users to stake their VAL coins within the Validity wallet. This staking mechanism not only bolsters the security of the network but also offers rewards to participants in the form of additional VAL coins. Examining further, the Validity Smartchain acts as a secondary layer above the main blockchain, enhancing scalability and providing advanced utilities. These utilities, which require payment in VAL, cover a diverse array of applications including Decentralized Identities (DID), Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), Social and Reputation Tokens, File Signing and Verification, and Decentralized Elections and Voting. In the broader cryptocurrency context, validity pertains to the authenticity and reliability of transactions and data on a decentralized platform. This ensures improved security, efficiency, and transparency. Nevertheless, potential challenges include price volatility, a lack of legal protections, and dependency on trusted intermediaries. The decentralized nature of the Validity network, coupled with its PoS consensus, highlights its dedication to security and efficiency. Users can participate in the network through staking, thereby strengthening its resilience and earning rewards. The advanced utilities offered by the Smartchain further establish Validity as a flexible participant in the blockchain ecosystem.
Investors interested in Validity are also interested in these Cryptos
This list presents a carefully selected selection of Cryptos that might be of interest to investors. We have our own crypto analyses for all listed Cryptos on Eulerpool.
Beginnings and the Rise of Cryptocurrencies
The history of cryptocurrencies began in 2008 when an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the whitepaper "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." This document laid the foundation for the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin. Bitcoin utilized a decentralized technology known as blockchain to enable transactions without the need for a central authority.
In January 2009, the Bitcoin network commenced with the mining of the Genesis Block. Initially, Bitcoin was more of an experimental project for a small group of enthusiasts. The first known commercial purchase using Bitcoins occurred in 2010, when someone spent 10,000 Bitcoins on two pizzas. At that time, the value of one Bitcoin was just fractions of a cent.
The development of other cryptocurrencies
Following the success of Bitcoin, other cryptocurrencies soon emerged. These new digital currencies, often referred to as "Altcoins," sought to use and improve blockchain technology in various ways. Some of the most well-known early Altcoins include Litecoin (LTC), Ripple (XRP), and Ethereum (ETH). Ethereum, founded by Vitalik Buterin, was particularly distinct from Bitcoin, as it enabled the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps).
Market Growth and Volatility
The cryptocurrency market grew rapidly, and with it public attention. The value of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies experienced extreme fluctuations. Highlights such as the end of 2017, when the Bitcoin price nearly reached 20,000 US dollars, alternated with sharp market crashes. This volatility attracted both investors and speculators.
Regulatory Challenges and Acceptance
As the popularity of cryptocurrencies rose, governments around the world began to grapple with the regulation of this new asset class. Some countries adopted a friendly stance and encouraged the development of crypto technologies, while others introduced strict regulations or outright banned cryptocurrencies. Despite these challenges, the acceptance of cryptocurrencies in the mainstream has steadily increased, with companies and financial institutions starting to adopt them.
Recent Developments and the Future
In recent years, developments such as DeFi (Decentralized Finance) and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) have broadened the range of possibilities offered by blockchain technology. DeFi enables complex financial transactions without traditional financial institutions, while NFTs allow for the tokenization of artwork and other unique items.
The future of cryptocurrencies remains exciting and uncertain. Questions about scalability, regulation, and market penetration remain open. Nevertheless, interest in cryptocurrencies and the underlying blockchain technology is stronger than ever, and their role in the global economy is expected to continue growing.
Advantages of Investing in Cryptocurrencies
1. High Return Potential
Cryptocurrencies are known for their high potential returns. Investors who got in early on projects like Bitcoin or Ethereum have made substantial gains. This high return makes cryptocurrencies an attractive investment opportunity for risk-seeking investors.
2. Independence from Traditional Financial Systems
Cryptocurrencies offer an alternative to the traditional financial system. They are not bound to the policies of a central bank, making them an attractive hedge against inflation and economic instability.
3. Innovation and Technological Development
Investing in cryptocurrencies also means investing in new technologies. Blockchain, the technology behind many cryptocurrencies, has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, from financial services to supply chain management.
4. Liquidity
Cryptocurrency markets operate around the clock, which means high liquidity. Investors can buy and sell their assets at any time, which is a clear advantage compared to traditional markets that are tied to opening hours.
Disadvantages of Investing in Cryptocurrencies
1. High Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are known for their extreme volatility. The value of cryptocurrencies can rise or fall quickly and unpredictably, posing a high risk to investors.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still emerging and varies greatly from country to country. This uncertainty can lead to risks, especially when new laws and regulations are introduced.
3. Security Risks
While blockchain technology is considered very secure, there are risks associated with the storage and exchange of cryptocurrencies. Hacks and fraud are not uncommon in the crypto world, which requires additional precautions.
4. Lack of Understanding and Acceptance
Many people do not fully understand cryptocurrencies and the underlying technology. This lack of understanding can lead to misguided investments. Additionally, the acceptance of cryptocurrencies as a means of payment is still limited.