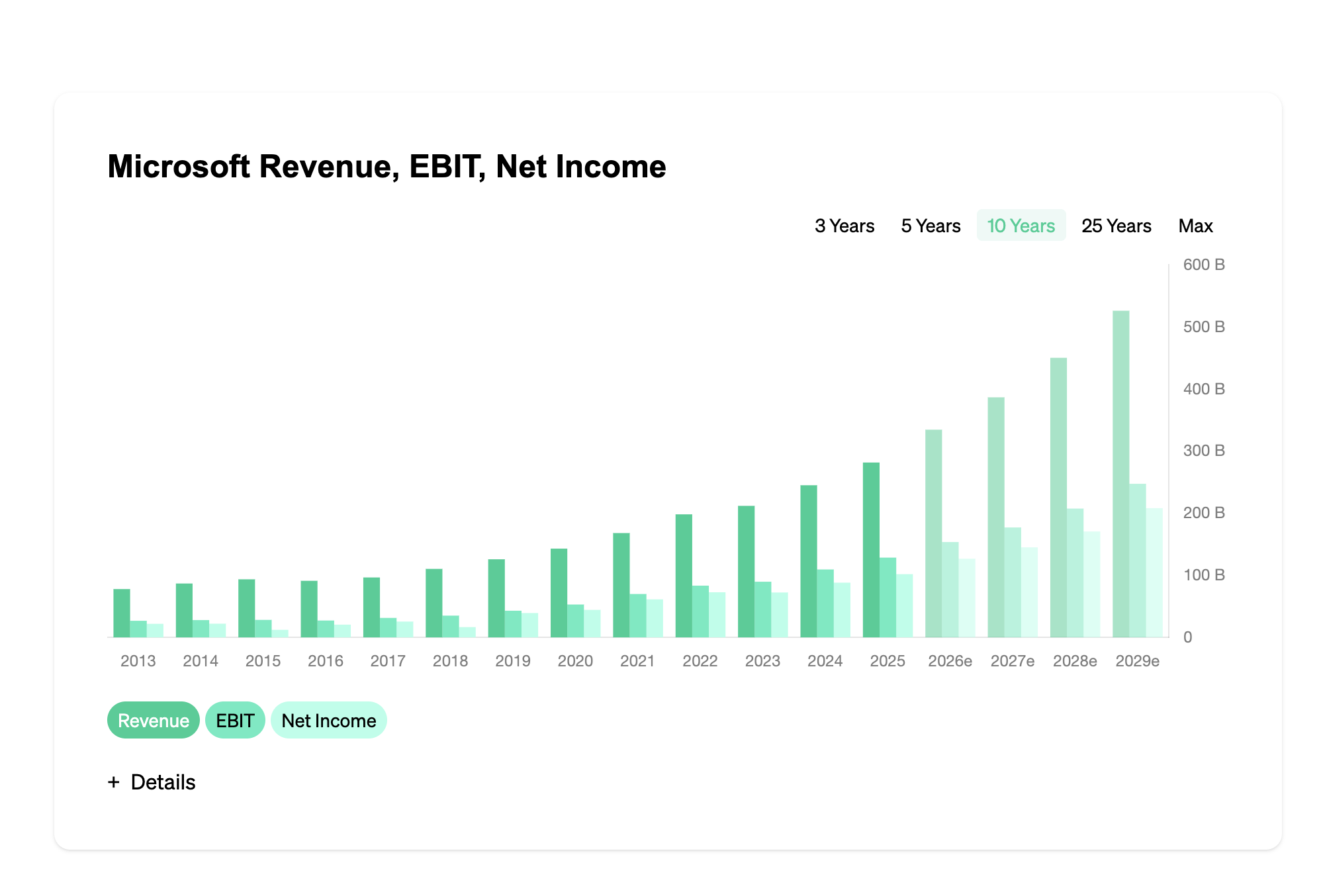
NIC
Definition und Erklärung
TL;DR – Kurzdefinition
Zu den FAQs →NIC: NIC is the acronym for Net Interest Cost, also known as Nettokostensatz in German. It is a significant measure utilized in capital markets, particularly within the realm of fixed-income securities. NIC represents the total borrowing cost to an issuer of a bond or loan after adjusting for the present value of all cash flows associated with the transaction, including any discounts or premiums. The calculation of NIC involves several key components. First, it takes into account the stated interest rate at which the bond or loan is issued. This rate is typically expressed as a percentage of the face value and determines the periodic interest payments made by the issuer. Secondly, NIC considers the time value of money by discounting those interest payments to their present value. This is accomplished by applying an appropriate discount rate, typically based on market interest rates or the specific credit risk of the issuer. Moreover, NIC incorporates any additional costs or rebates associated with the issuance of the bond or loan. Such costs may include underwriting fees, commissions, legal expenses, or other administrative charges. The inclusion of these expenses ensures the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the overall borrowing cost estimation. Investors heavily rely on NIC to gauge the true expense associated with fixed-income investments. By considering all relevant costs and present valuing future cash flows, NIC provides a reliable benchmark to compare different investment opportunities within the capital markets. This allows investors to make informed decisions based on the net cost to the issuer and the potential yield or return they can expect from the investment. In summary, Net Interest Cost (NIC) measures the total borrowing cost for an issuer of a bond or loan, accounting for the present value of all cash flows, adjustments, and additional costs incurred during the transaction. By evaluating the NIC, investors gain valuable insight into the actual expenses associated with fixed-income investments, aiding them in making informed investment decisions. At Eulerpool.com, a premier destination for equity research and finance news, we strive to provide the most comprehensive and accurate glossary/lexicon for investors in capital markets. Be sure to explore our website for further information and an extensive range of resources tailored to your investment needs.
Ausführliche Definition
Häufig gestellte Fragen zu NIC
Was bedeutet NIC?
NIC is the acronym for Net Interest Cost, also known as Nettokostensatz in German. It is a significant measure utilized in capital markets, particularly within the realm of fixed-income securities.
Wie wird NIC beim Investieren verwendet?
„NIC“ hilft dabei, Informationen einzuordnen und Entscheidungen an der Börse besser zu verstehen. Wichtig ist immer der Kontext (Branche, Marktphase, Vergleichswerte).
Woran erkenne ich NIC in der Praxis?
Achte darauf, wo der Begriff in Unternehmensberichten, Kennzahlen oder Nachrichten auftaucht. In der Regel wird „NIC“ genutzt, um Entwicklungen zu beschreiben oder Größen vergleichbar zu machen.
Welche typischen Fehler gibt es bei NIC?
Häufige Fehler sind: falscher Vergleich (Äpfel mit Birnen), isolierte Betrachtung ohne Kontext und das Überinterpretieren einzelner Werte. Nutze „NIC“ zusammen mit weiteren Kennzahlen/Infos.
Welche Begriffe sind eng verwandt mit NIC?
Ähnliche Begriffe findest du weiter unten unter „Leserfavoriten“ bzw. verwandten Einträgen. Diese helfen, „NIC“ besser abzugrenzen und im Gesamtbild zu verstehen.
Læserfavoritter i Eulerpool Børsleksikon
Annehmlichkeit
"Dentons is the world's largest law firm, delivering quality and value to clients around the globe. Dentons is a leader on the Acritas Global Elite Brand Index, a BTI Client...
Stille Reserve
Stille Reserven sind ein Begriff aus der Finanzwelt, der sich auf latent vorhandene Gewinne innerhalb eines Unternehmens bezieht, die nicht in den offiziellen Buchhaltungsunterlagen erfasst sind. Diese geheimen oder stillen...
Sparkassenreglement
Sparkassenreglement ist eine gesetzlich vorgeschriebene Geschäftsordnung für Sparkassen, die in Deutschland als öffentlich-rechtliche Institute agieren. Als grundlegender Leitfaden für das operative Geschäft legt das Sparkassenreglement die internen Abläufe, Zuständigkeiten, Richtlinien...
MAI
MAI steht für "Markt für Alternative Investmentfonds" und bezieht sich auf einen spezifischen Markt in Deutschland für Anlageprodukte, die nicht in herkömmliche Anlagen wie Aktien, Anleihen oder Geldmarktinstrumente investieren. Stattdessen...
Fachhandelsbindung
Fachhandelsbindung bezeichnet eine Vertriebsstrategie, bei der ein Hersteller oder Großhändler seine Produkte ausschließlich an spezialisierte Einzelhändler verkauft. Dabei entsteht eine enge Partnerschaft zwischen dem Hersteller und den Fachhändlern, die sowohl...
Anwartschaftsrecht
Das Anwartschaftsrecht ist ein juristischer Begriff, der im Zusammenhang mit dem Eigentumsübergang oder Erwerb von Vermögenswerten verwendet wird. Es bezieht sich auf das Recht einer Person, einen künftigen Anspruch auf...
Vollkosten
Vollkosten sind ein wesentlicher Bestandteil der Kostenkalkulation und ermöglichen ein umfassendes Verständnis der Gesamtkosten für ein Produkt oder eine Dienstleistung. Im Bereich der Kapitalmärkte bezieht sich der Begriff Vollkosten vor...
Zollverwaltung
Zollverwaltung ist ein Begriff, der in der Welt des internationalen Handels und der Kapitalmärkte von großer Bedeutung ist. Die Zollverwaltung bezieht sich auf die abwickelnden Tätigkeiten und Aufgaben, die von...
umgekehrte Maßgeblichkeit
Umgekehrte Maßgeblichkeit bezieht sich auf eine wichtige steuerliche Regelung, die in Deutschland angewendet wird. Diese Regelung betrifft die Besteuerung von Kapitalgesellschaften und stellt sicher, dass Gewinne, die von Tochtergesellschaften an...
Exoskelett
Das Exoskelett ist ein hochentwickeltes technologisches Gerät, das zur Verbesserung der körperlichen Leistungsfähigkeit und Unterstützung des Bewegungsapparats entwickelt wurde. Es wird häufig in Branchen wie der Schwerindustrie, dem Militär und...