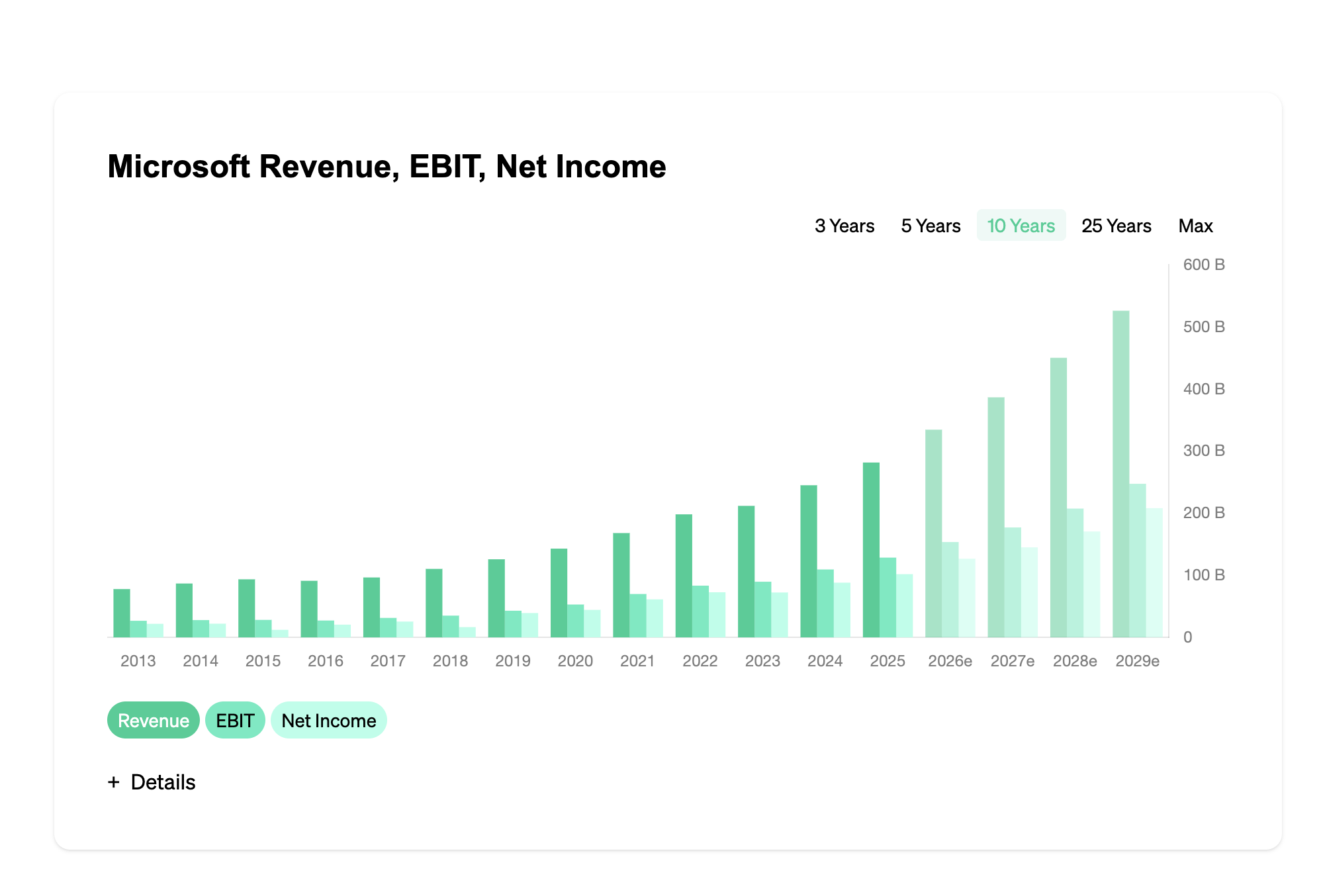
Floating Rate Note (FRN)
Definition and Explanation
TL;DR – Brief Definition
Go to FAQs →Floating Rate Note (FRN): Floating Rate Notes (FRNs), commonly known as Floater Bonds, are debt instruments with variable interest rates that are adjusted periodically, making them responsive to changes in market conditions. These securities are issued by various entities, including governments, corporations, and financial institutions, to raise capital. Unlike fixed-rate bonds, FRNs provide investors with the opportunity to benefit from shifting interest rates. Floating Rate Notes typically have a two-fold structure consisting of a reference interest rate, such as LIBOR (London InterBank Offered Rate), and a fixed spread. The reference interest rate, which serves as a baseline, is periodically reset based on prevailing market rates. The fixed spread, on the other hand, remains constant for the duration of the FRN. The sum of these two components determines the interest payable to bondholders. The main advantage of investing in Floating Rate Notes is their ability to mitigate interest rate risk. Since their interest payments adjust periodically, FRNs offer protection against adverse movements in interest rates. As rates rise, the coupon paid to investors also increases, ensuring a relatively stable investment return even in volatile markets. This characteristic makes FRNs an attractive investment option when interest rates are expected to rise. Additionally, the floating rate structure of these notes serves as a hedge against inflation. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-rate investments, such as traditional bonds. However, by linking interest payments to prevailing market rates, FRNs provide investors with a potential safeguard against inflationary pressures. Floating Rate Notes are generally more complex than fixed-rate bonds, requiring investors to carefully evaluate the creditworthiness of issuers before investing. Credit rating agencies play a significant role in assessing the credit quality of FRNs, providing investors with a measure of the issuer's ability to meet its debt obligations. Higher-rated FRNs generally offer lower yields due to their lower credit risk.
Detailed Definition
Frequently Asked Questions about Floating Rate Note (FRN)
Was bedeutet Floating Rate Note (FRN)?
Floating Rate Notes (FRNs), commonly known as Floater Bonds, are debt instruments with variable interest rates that are adjusted periodically, making them responsive to changes in market conditions. These securities are issued by various entities, including governments, corporations, and financial institutions, to raise capital.
Wie wird Floating Rate Note (FRN) beim Investieren verwendet?
„Floating Rate Note (FRN)“ hilft dabei, Informationen einzuordnen und Entscheidungen an der Börse besser zu verstehen. Wichtig ist immer der Kontext (Branche, Marktphase, Vergleichswerte).
Woran erkenne ich Floating Rate Note (FRN) in der Praxis?
Achte darauf, wo der Begriff in Unternehmensberichten, Kennzahlen oder Nachrichten auftaucht. In der Regel wird „Floating Rate Note (FRN)“ genutzt, um Entwicklungen zu beschreiben oder Größen vergleichbar zu machen.
Welche typischen Fehler gibt es bei Floating Rate Note (FRN)?
Häufige Fehler sind: falscher Vergleich (Äpfel mit Birnen), isolierte Betrachtung ohne Kontext und das Überinterpretieren einzelner Werte. Nutze „Floating Rate Note (FRN)“ zusammen mit weiteren Kennzahlen/Infos.
Welche Begriffe sind eng verwandt mit Floating Rate Note (FRN)?
Ähnliche Begriffe findest du weiter unten unter „Leserfavoriten“ bzw. verwandten Einträgen. Diese helfen, „Floating Rate Note (FRN)“ besser abzugrenzen und im Gesamtbild zu verstehen.
Favoritos de los lectores en el Börsenlexikon de Eulerpool
Kostenzurechnungsprinzipien
Kostenzurechnungsprinzipien beschreiben die Grundsätze und Verfahren, nach denen Kosten auf bestimmte Kostenträger, wie Produkte, Dienstleistungen oder Geschäftsbereiche, zugerechnet werden. Diese Prinzipien sind von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die tatsächlichen Kosten und...
Absatzwirtschaft
Absatzwirtschaft ist ein Begriff, der in der Welt der Kapitalmärkte häufig Verwendung findet und einen essentiellen Bestandteil des Unternehmenserfolgs darstellt. Dieser Begriff bezieht sich auf die Disziplin der Marketingwissenschaft, die...
Versammlungsfreiheit
Versammlungsfreiheit ist ein Grundrecht, das in der deutschen Verfassung verankert ist und das Recht auf Frieden und friedliche Versammlungen gewährleistet. Es ist ein wichtiger Aspekt des demokratischen Systems und ermöglicht...
Überlappung
Die "Überlappung" ist ein Begriff, der in den Kapitalmärkten häufig verwendet wird und sich auf eine Situation bezieht, in der zwei oder mehrere Ereignisse, Trends oder Indikatoren zeitlich miteinander verknüpft...
Lucas
"LUCAS" steht für "Logical Unit for Communication and Analysis of Securities" und ist ein hochmodernes und innovatives System im Bereich der Kapitalmärkte. Dieses System wurde entwickelt, um Investoren und Finanzprofis...
endogenes Wachstum
Definition: "Endogenes Wachstum" ist ein Begriff aus der Wirtschaftstheorie, der das Konzept des langfristigen, internen und nachhaltigen wirtschaftlichen Wachstums beschreibt. Es bezieht sich auf die Fähigkeit einer Volkswirtschaft, ihr BIP...
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
Die Secure Socket Layer (SSL) ist ein Verschlüsselungsprotokoll, das in der Informationssicherheit verwendet wird, um die Vertraulichkeit und Integrität von Daten, die über das Internet übertragen werden, zu gewährleisten. Dieses...
Dienstleistungskosten
Definition of Dienstleistungskosten: Die Dienstleistungskosten beziehen sich auf die Gebühren, die zur Erbringung von bestimmten Dienstleistungen anfallen. Im Kontext der Kapitalmärkte, insbesondere im Bereich der Aktien-, Kredit-, Anleihe-, Geldmarkt- und Kryptowährungsmärkte,...
Altlasten
Altlasten bezieht sich auf die Verbindlichkeiten oder finanziellen Belastungen, die auf einem Unternehmen oder einer bestimmten Anlageklasse lasten. In der Finanzwelt wird der Begriff häufig verwendet, um auf Unternehmensverschuldung, faule...
Deport
Definition: "Deport" (auf Deutsch: "Deponieren") ist ein Begriff, der in Bezug auf den Kapitalmarkt verwendet wird und sich auf die Übertragung von Wertpapieren oder Assets von einem Depot auf ein...